Cartographica has a number of powerful facilities to provide for geospatial analysis and feature attribute propagation, among these is the powerful Spatial Join operation.
Spatial Joins are used to combine the data attributes of two or more layers. The Spatial Join operation creates a new layer that is a combination of attributes from Join and Target layers. The Spatial Join functions are akin to the Overlay functions except that the Spatial Join procedure does not change the geometry of the layers. Spatial Joins can be used for many different purposes and there are many options for determining how the join will be processed.
A Spatial Join can be performed on point, line, or polygon layers. The resulting vector layer will match the Selected layer's data format (i.e. point, line, or polygon). For example, if you select a polygon layer and then perform a Spatial Join (using an Intersect function) with a point layer as the Join layer, the output would be a polygon layer with attribute data joined from the point layer. In this case one attribute added to the polygon layer would be a count of the number of points that intersected with each polygon in the Selected layer.
The default Spatial Join option is the Intersection function, which will join two layers that overlap in space. In addition to the Intersection function there are 15 additional methods for performing Spatial Joins that can be used to fit various situations.
Table 8.2. Spatial Join Operations
Spatial Join Operation | Description | Suitable Geometry |
|---|---|---|
Intersecting | Selected layer feature intersects join layer feature at any point | Any and Any |
Intersecting (3D) | Selected layer feature intersects join layer featureat any point (3D) |
Any and Any |
Within Distance | Selected layer feature is within distance of join layer feature at any point | Any and Any |
| Within Distance (3D) | Selected layer feature is within distance of join layer feature at any point (3D) | Any and Any |
Contains | Selected layer feature contains any portion of the join layer feature (differs from intersection in that touching only at boundaries is excluded) | Polygons may contain Any Lines may contain lines or points Points may not be the selected layer. |
Completely Contains | Selected layer feature contains all the join layer feature |
Polygons may contain Any Lines may contain lines or points Points may not be the selected layer. |
Within | Selected layer feature is within if contained within the join layer feature. Effectively Contains, but with the opposite result layer | Polygons may be within Polygons Lines may be within Lines Points may be within Lines or Polygons |
Completely Within | Selected layer feature is within if completely contained within the join layer feature. Effectively Completely Contains, but with the opposite result layer |
Polygons may be within Polygons Lines may be within Lines Points may be within Lines or Polygons |
Within (Clementini) | Selected layer feature contains all of the join layer feature, but the join layer must be at least partially within the body of the selected layer feature (i.e. cannot only be coincident with the edge). | Polygons may contain Any Lines may contain Lines or Points Points may not be the selected layer. |
| Identical To | Selected layer feature is identical to the join layer feature | Any may be identical to the same |
Touches Boundary | Selected layer feature touches the join layer feature (but does not cross). | Any and Any |
Shares a line segment | Selected layer feature shares a line segment with the join layer feature. | Polygon or Line and Polygon or Line |
| Crossed by the Outline | Selected layer feature is crossed by the outline of the join layer feature. | Polygon or Line and Polygon or Line |
Have Center Within | Selected layer feature's center falls within the join layer feature. (Center for point is the point; for line is the midpoint; for multipoint or polygon is the centroid) | Any and Any |
Closest | The join layer feature closest to the selected layer feature. | Any and Any |
Join Parameters
In addition to the Spatial Join Operation, there are a few parameters that modify the behavior of the operations:
Maximum Distance defines the maximum distance for the distance operations (Within Distance, Within Distance (3D) and Closest).
Distance Column Name defines the column name of a column to contain the distance when used with any of the distance operations (if left blank, no distance will be stored).
One Feature per Match, if checked, generates a new copy of the Selected layerfeature for each match with a Join Layer feature.
Discard Unmatched Features, if checked, will not generate a Selected Layer feature in the event that there is no match with the Join Layer feature.
Field Mapping
The Field Mapping box determines the mapping between the incoming fields (from both the Selected layer and the Join layer) as well as a few special calculated columns. The table shows the following columns, in order:
Operation The operation to perform and store in this output column
Table 8.3. Field Mapping Operation
Operation Result Copy Matching feature's data will be copied Ignore No column will be created Min Minimum value of matching features' data Max Maximum value of matching features' data First Value of first matching feature's data Last Value of last matching feature's data Sum Sum of matching features' data Average Average of matching features' data Count Count of matching features with data Sigma Sigma calculation of matching features' data Layer The original layer that the data comes from.
Original Name The name of the original column that the data comes from
Output Name The name of the output column
Ratio When checked, this indicates to calculate any value based on the ratio of the combined feature (only valid for the numeric operations). In particular, this checkbox will multiply the column value times the area (in case of the polygon) or length (in case of a line) in the join feature relative to the join features entire area or line. This is only relevant to the Intersection, Contains, Within operations for polygons and some boundary operations with lines.
It is possible to create additional output columns for the same original field. To do this, select the desired field and choose from the pop-up menu by using ctrl-click. This can be handy when you need multiple numeric calculations on the same original column. |
In addition to the fields from the Selected and Join layers, there are 3 specialized columns that are automatically created:
JOIN_FID The feature ID of the join layer feature
TARGET_FID The feature ID of the selected layer feature
Join_Count The number of join features that matched this selected layer feature. If One Feature per Match is checked, then this should never be more than 1.
Using Spatial Join
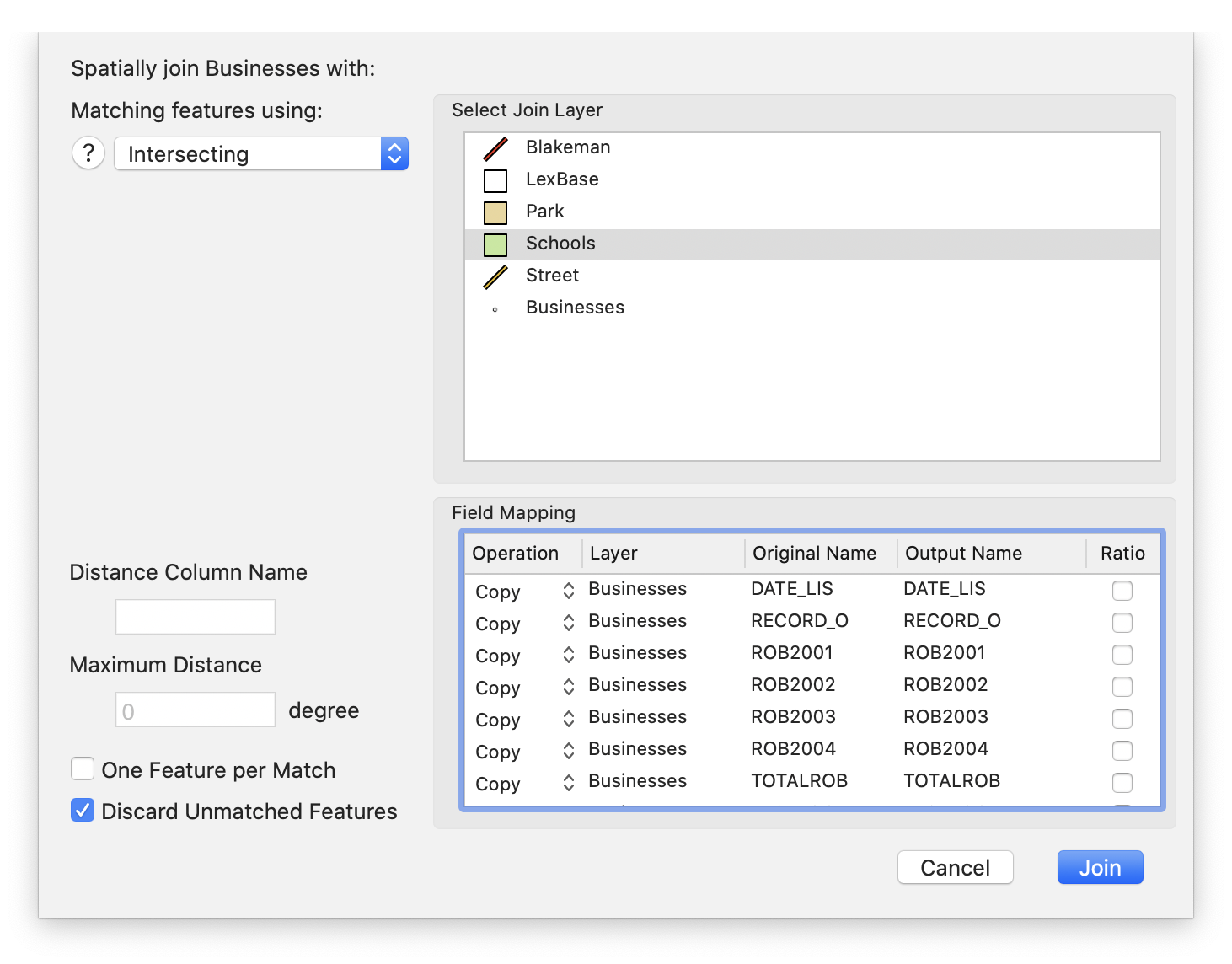
Select the layer you want to use as the primary layer. This is the one from which features will be copied to the result layer.
Choose > .
The Spatial Join sheet appears
Choose from one of the Spatial Join operations (discussed previously in Table 8.2, “Spatial Join Operations”)
Select the join layer in Select Join Layer box.
Make desired changes to the output fields in the Field Mapping box
Click