Buffers are a very common and useful tool employed for data analysis. In it's simplist form, a buffer is an area created around a feature (point, line or polygon) which keeps the basic shape of the original feature, but expands the size of the feature by some amount.
Buffers are often used around points to create a survey area. For example, you might create a buffer of 500 ft radius around a set of points representing schools in order to analyze the number of banks within 500 ft of schools.
Under some circumstances, negative buffers (buffers which are inset from the border of a polygon) are used to determine internal information about a set of polygonal features. Negative buffers may not be used with points or lines.
VISUAL EXAMPLE
Create Buffers
Select the features you want to create the buffer around
Choose >
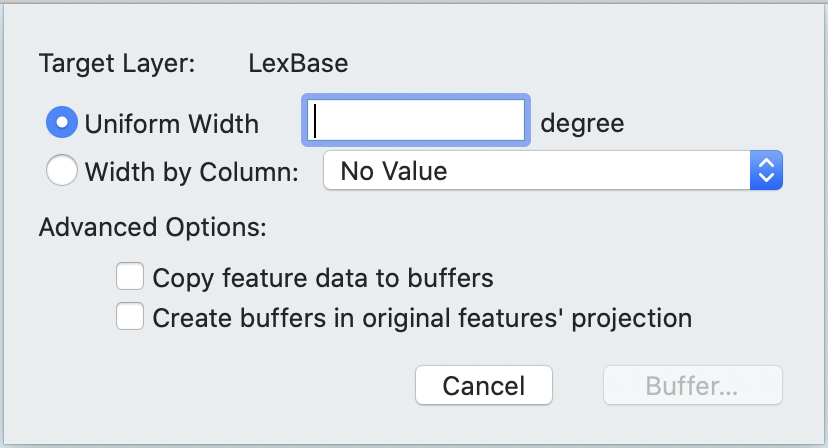
The Create Buffers sheet appears.
If you want to create buffers in the coordinate system of the original features instead of the map, check the box next to Create buffers in original features' projections. This is not a common operation, as it can cause the buffers to appear irregularly shaped.
Choose your buffer distance:
Select the distance that the buffer is created around the features as a number (using the Uniform Width field. Units will be displayed to the right of the box and if the units are linear, it is possible to set the units using the pop-up menu next to the box.
Select the distance that the buffer is created around the features as a Width by Column to have the current value the specified column determine the radius.
Cartographica currently expects this column size to be scaled to the units of the layer. In the case of latitude and longitude, that's degrees, in other cases commonly feet or meters. The units will be displayed, and if the units are linear, it will be possible to change them using the pop-up menu next to the Uniform Width box.
Check Copy Feature Data to Buffer if you want each attribute of the feature being buffered to be copied to the resultant buffer.
Click .
Cartographica creates a buffer area around the points, lines, or polygons that are in the selection or selected layer and saves them into a new layer.
Very large and complex geometries with small buffer sizes can take a long time to resolve.